Bottom Line - Pros and cons of lab-grown diamonds:
If you’re just stopping by for the key points, here they are:
Pros:
- Lab-grown diamonds share the same chemical and physical characteristics as natural diamonds. The main difference is the origin.
- Both trained and untrained eyes can’t distinguish between natural and lab-created diamonds. They look the same.
- You can save 50%-70% of your money by getting a lab-grown diamond with the same grades as your ideal natural diamond.
- With the same amount of money, you can get a larger and better lab-grown diamond than a natural diamond.
- Lab-grown diamonds are also known as sustainable diamonds and are much more eco-friendly than mined diamonds.
Cros:
- Some customers are still skeptical. They look at natural diamonds as more luxurious and valuable (keep reading to discover why this legitimate assumption is wrong.)
- Some customers feel like it’s “real diamonds vs. fake diamonds,” even though they share identical chemical and physical characteristics.
- Looking for a natural diamond? BEWARE of scammers trying to sell you a lab-grown diamond and make you think it’s natural. Make sure to buy your diamond, both natural and lab-grown, from a reliable seller only.
Consider buying lab-grown diamonds from a reputable source like the one mentioned to guarantee an authentic purchase. This specific vendor provides both GIA and IGI certified lab-grown diamonds. For those in search of a more extensive array of GIA lab-grown diamonds, turn your attention to this subsequent retailer. Recognized for their trustworthiness, they hold the largest assortment of lab-grown GIA certified diamonds in the industry.
Deal Alerts!
RECOMMENDED RELIABLE SELLERS ONLY.
Up to 50% OFF Selected Jewelry at Blue Nile
Instant $100 off when signing up + 3% discount on wire transfer at Whiteflash
Table of Contents
As lab-grown diamonds gain more popularity, more and more customers consider shifting to this alternative product. Overall, these diamonds are more eco-friendly and affordable than mined ones. In this article, we will cover the pros and cons of lab-grown diamonds. My goal here is to help you understand whether or not a lab-grown diamond can be the right choice for you.
Without further ado, let’s get straight to it:
Pros of Lab-Grown Diamonds
1. The first advantage is cost-saving. Lab-grown diamonds are naturally more affordable than their mined counterparts. The price difference is enormous compared to natural diamonds. We can find around a 70% price gap on some diamonds. This allows you to save 70% of your money by picking a lab-grown diamond with equal grades or investing more and getting a better-looking, larger diamond.

2. The second advantage is environmental conservation. Unlike natural diamonds, these diamonds aren’t obtained through mining which is one of the major culprits of environmental degradation. Instead, they are produced in the laboratory where environmental preservation methods and practices are strictly observed.
3. Besides providing cost-saving and environmental conservation benefits, lab-grown diamonds are generally more visually appealing than their mined counterparts. That’s because, unlike the latter, they result from a process free from all possible impurities. Nitrogen atoms and other soil impurities can affect the purity and clarity of natural diamonds, lowering their aesthetic quality slightly.

Additionally, lab-created diamonds are cheaper to produce compared to natural diamonds. You probably know that mining is one of the most expensive commercial undertakings out there. Fortunately, this process doesn’t involve any of it. Instead, it just entails extracting carbon atoms from carbon compounds and subjecting them to immense heat and pressure to form crystallized carbon particles that constitute diamonds. The machines and techniques needed to accomplish that are cheaper than those required to mine natural diamonds deep beneath the earth’s surface.
4. Finally, lab-grown diamonds are non-depletable and hence sustainable, unlike their natural counterparts. That’s because carbon atoms, their main ingredient, can be extracted from carbon dioxide, a gas that will never deplete from the atmosphere, at least as far as humans, animals, and plants exist on this planet. That means as long as the means to extract and crystalize these atoms are there, one can always make artificial diamonds.
Cons of Lab-Grown Diamonds
1. Unfortunately, growing diamonds in the lab can be pretty energy-demanding. This can lead to high energy bills, putting significant financial strain on the business. However, as technology evolves, energy consumption also decreases (which is a good thing!)
2. While the cheaper price tags of lab-grown diamonds compared to natural diamonds can be a great thing for some buyers, other customers may see it as less luxurious.
3. For diamond dealers that sell natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds are simply bad for business. Think about it like dairy and soy milk: some customers prefer to get an alternative product, which makes the dairy industry has a smaller market share. The same goes here: Many customers prefer an eco-friendly, larger, nicer lab-grown diamond for a much better price.
4. Lastly, many unsuspecting buyers have lost their hard-earned cash by buying lab-grown diamonds while thinking they are natural. It’s a common scam. When buying a natural diamond, ensure it’s certified by a legitimate grading lab such as the IGI/AGS/GIA. I strongly recommend buying only from a reliable seller. Remember that a cheap price may cost you later. As much as I love finding good deals, we need to draw the line when it’s too good to be true.
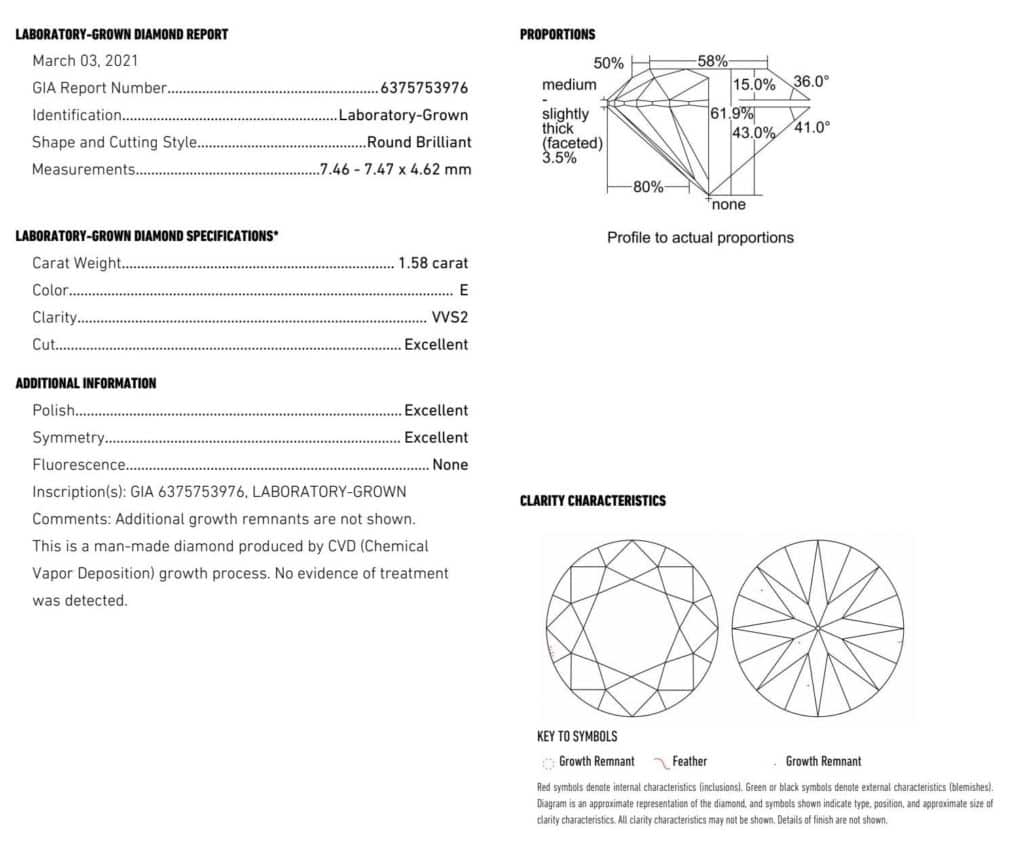
GIA certificate:
What Is a Lab-Grown Diamond?
Also known as a lab-created diamond, a lab-grown diamond is a diamond that’s made in the laboratory. The process involves extracting carbon atoms from the air or a carbon-rich substance and gradually converting them into a crystalline form—crystalized carbon. This can take anywhere between 4-10 weeks.
Four techniques can be used in carbon crystallization;
- High pressure, high temperature (HPHT) technology.
- Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology.
- Detonation synthesis technology—entails creating nanometer-sized diamond grains through the detonation of carbon-containing explosives.
- High-power ultrasound graphite treatment technology—involves treating graphite with high-power ultrasound.
N/B: Of all the above techniques, HPHT and CVD remain popular. Nonetheless, lab-created diamonds made using the first technology are called “HPHT diamonds,” and those created through the second technology are known as “CVD diamonds.”
Unfortunately, producing artificial diamonds requires a lot of energy, which could explain why not so many countries involve themselves in this activity. Only a few countries like China, the USA, Russia, South Africa, Ireland, Japan, Belarus, Sweden, Ukraine, Israel, and France do, with China topping the list. According to the BBC, it’s the world’s most populous country and produces 50 to 60 percent of artificial diamonds.
How Are Lab-Created Diamonds Made?
As I stated earlier, lab-created diamonds are created using diverse methods with HPHT and CVD being predominant. In each process, a “diamond seed” and a carbon compound are key. For starters, the “diamond seed” is a crystalline form of carbon. It can be derived from an actual diamond and most labs get theirs from their previously created diamonds (usually those with the most desirable properties). The carbon compound, on the other hand, is a substance that contains a mixture of carbon and other chemical elements.
1. The High Pressure, High-Temperature Method
In the high pressure, high-temperature method, the carbon compound is placed at the bottom of a belt press, cubic press, or split-sphere (BARS) press. After that, immense pressure (of up to 730,000 PSI) and heat(beyond 2,550 °F or 1,400 °C) are supplied, completely melting it. The molten carbon compound results in pure carbon residues, which are then sent to the diamond seed. This eventually grows into a diamond after about 4-10 weeks.
2. The Chemical Vapor Deposition Method
In the CVD method, diamonds are grown from a hydrocarbon gas mixture and a diamond seed. This technique entails using a gas chamber, immense heat, a carbon-rich gas (often methane gas), and a sophisticated microwave or laser machine.
The diamond seed is placed in the gas chamber, which is then sealed and heated to around 800 degrees Celsius (1472°Fahrenheit). After that, the gas is smoked into the sealed chamber and ionized into plasma using the microwave or laser machine. This process gradually breaks the carbon away from the gas. The resultant carbon atoms find and adhere to the diamond seed, slowly building up into a crystal diamond, atom by atom.
Are Lab-Grown Diamonds as Good as Natural Diamonds?
The short answer is yes because both have the same visual qualities and physical properties. In some cases, lab-grown diamonds can look more sparkling than their natural counterparts due to the absence of impurities like nitrogen atoms, unlike the latter.
It all boils down to how the crystallization of the carbon atoms takes place in both cases. Remember that diamonds are fundamentally made up of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal structure known as “diamond cubic.”
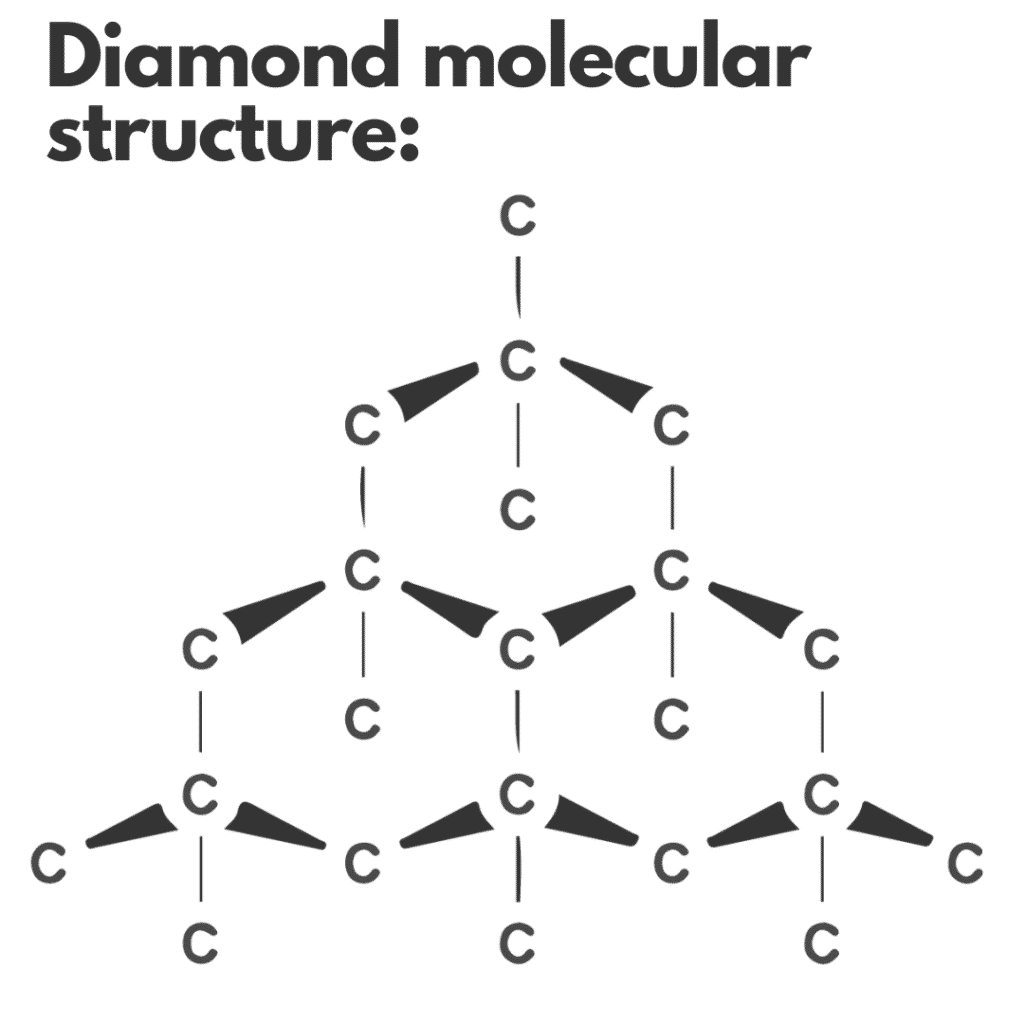
Carbon atoms have crystallized and arranged themselves in the above structure in both natural and artificial diamonds due to immense heat and pressure. However, in the former case, this process has occurred naturally in a non-controlled environment (hundreds of meters beneath the earth’s surface) after millions of years. Consequently, it has been affected by many issues, including impurities like hydrogen atoms.
Did you know?...
a) Soil is a material made up of several things, including organic matter, minerals, living organisms, water, and gas.
b) The organic matter chiefly consists of nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and smaller quantities of sulfur plus other elements.
c) Nitrogen is arguably the most common impurity found in natural diamonds, comprising up to 1% of the gemstone by mass.
When it comes to lab-created diamonds, however, the carbon crystallization process has taken place in a controlled environment(in the laboratory). Here state-of-the-art equipment ensures maximum precision, eliminating the issue of impurities getting into the gradually crystallizing carbon atoms.
Can An Untrained Eye Tell If a Diamond is Lab-Created? Can a Jeweler Tell?
To answer the first and second questions, no. That’s because lab-grown diamonds have visual characteristics and qualities similar to natural diamonds. That makes it almost impossible to distinguish the diamonds at a glance. However, lab-created diamonds have zero nitrogen atoms, while natural diamonds have tiny amounts of those atoms, which can only be detected by particular devices. Instead of relying on the naked eye, professional gemologists and jewelers will use those devices to test the diamond’s fluorescence and tell whether the diamond is lab-grown or mined, based on the presence or absence of those atoms.

Is a Lab-Grown Diamond Right For You?
The answer depends on a few factors. You see, lab-created diamonds are just as real as their natural counterparts mined from the earth. Both have similar physical and chemical properties, in other words, the same shape, sizes, color grades, and clarity grades.
However, lab-grown diamonds tend to be assigned a lower value compared to natural diamonds. If you don’t care about the monetary value disparity between the two choices, a lab-grown diamond will just be as good. If it’s a jewelry piece, it will allow you to make a fashion statement just as a jewelry piece made from mined diamonds.
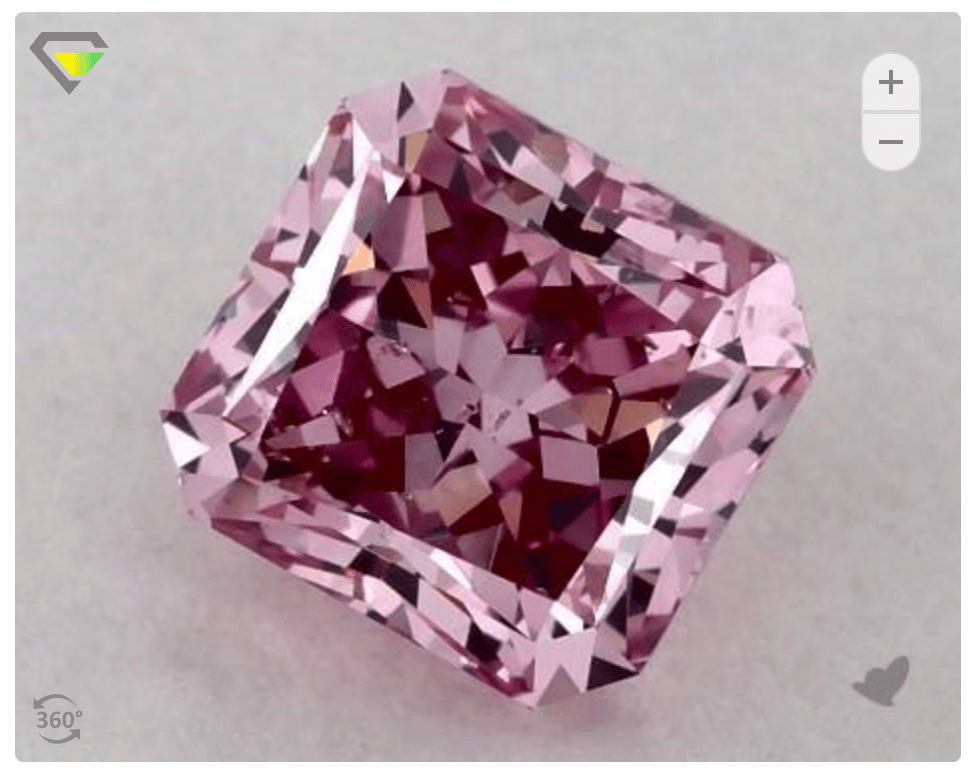
The argument about lab-grown diamonds’ resale value doesn’t hold water either. Most natural diamonds will lose 40%-60% of their value the second you pay for them. Only scarce diamonds, for example, fancy blue, pink and red, will maintain or raise their value in the long term.
Check this 1.02 carat fancy pink diamond (Click on the image to see its price tag)
My point is, when buying a diamond engagement ring, focus on making your loved one happy. Moneywise, a lovely 2000s Rolex Submariner, can give you a better return 🙂
Conclusion
Finally, people are starting to embrace lab-grown diamonds as real diamonds. Many celebrities no longer have a problem wearing jewelry pieces made out of these diamonds. The beauty of these sustainable diamonds is that they are just as real as their mined counterparts with which they share chemical and physical qualities. Both consist of crystallized carbon atoms.
In natural diamonds, carbon atoms have naturally crystallized under the surface of the earth due to the impact of immense heat and pressure for millions of years. In artificial diamonds, on the other hand, the atoms have been crystallized in the laboratory for a short period of between 4-10 weeks by using special technologies. Both types of diamonds have their advantages and disadvantages as highlighted above.
People also ask:
Lab-grown diamonds vs. natural diamonds full comparison
Are lab diamonds GIA certified?
IGI lab-grown diamonds: Are they legit?
Are lab diamonds ethical and eco-friendly?
CVD vs HPHT lab-grown diamonds: What is the difference?
Are lab-created diamonds and moissanite the same?
Lab-grown diamonds resale value: Are lab-created diamonds worth anything?
Which color is the best for lab-grown diamonds?
What are the pros and cons of lab-grown diamonds?
Do lab diamonds test as real diamonds?
Are lab-grown diamonds and cubic zirconia the same?
When were lab diamonds first created?
Which clarity is best for your lab-grown diamond?